FAQS
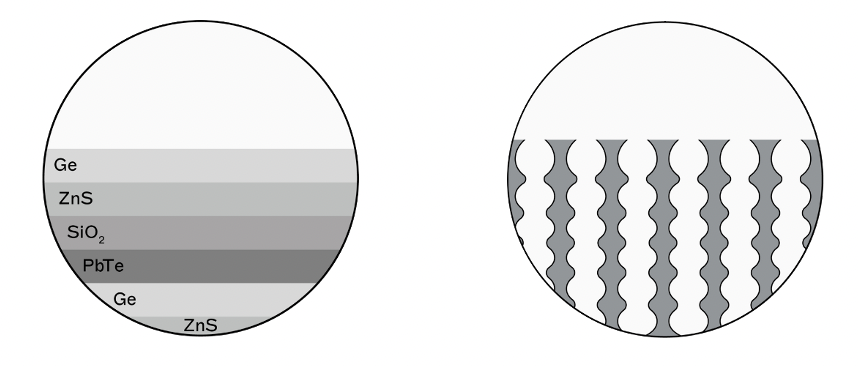
Our filters are totally different from our competence.
Those are multilayer, and ours are based in macroporous technology.
The manufacturing process is called electrochemical etching and consists in drilling micrometric holes, or pores, in a silicon substrate by a wet etching with acid and water as main components.
In concrete, the silicon substrate is inserted in a cell and the rear part of the wafer faces a LED array.
The other surface (where pores are going to be homogenously etched) is in touch with the electrolyte.
In the rear part electron-hole pairs are created thanks to LED illumination and holes travel till the other surface where they react with the solution and etch very precisely the silicon.
In such a way we create 3D structures of air inside the silicon and we can control the light propagation through it.
Our all-silicon technology gives our filters outstanding characteristics, such as high robustness to harsh environments and better optical qualities as well as low costs processes.
- Robustness to harsh environments:
- Temperature: we are not limited by adhesion problems between layers. In multilayer filters there are different expansion coefficient between materials. Therefore, at higher temperatures than 80 ºC they start to experiment tensions between layers that eventually peels the filters or breaks their surface. Macroporous silicon can be heated until 200 ºC without previous problems.
- Humidity: they are hydrophobic. There is no variation in the optical properties of silicon in presence or water vapor.
- Scratching: they can be cleaned with paper or towels and they do not scratch. Also, they can be cleaned using ethanol, with no variation of their features.
- Any shape you need without extra cost or loss of optical characteristics
- Small batches, less developing costs
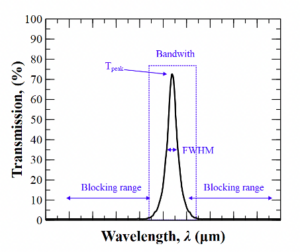
- Central Wavelength: describes the midpoint of the spectral bandwidth over which the filter transmits.
- Bandwidth: wavelength interval used to designate the part of the spectrum that transmits through a filter.
- FWHM: Full Width Half Maximum, wavelength range limited at both sides for those wavelengths where the filter achieves 50% of the maximum transmission.
- Transmittance: percentage of incident light passing through the filter
- Blocking range: spectral region that is attenuated by the filter. The degree of its blocking is usually specified in terms of optical density.
The optical density describes the amount of energy blocked (no transmitted) by the filter in a specific range. In neutral density filters this block is ideally uniform over the entire range.
The OD formula is:
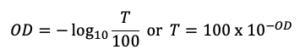
Typical ODs are
- OD 1: 10% transmission
- OD 1.3: 5% transmission
- OD 2: 1% transmission
- OD 3: 0.1% transmission
You may send your request to sales@mapsi.es. Mapsi sales staff will contact you as soon as possible (within one to two business days).
You can also design your own filter and, upon completion, the filter you want will be sent directly to us!
Easy. Go to ‘Design your own filter’ and follow the instructions!
For additional information, please contact info@mapsi.es